Introduction
The world of finance is a complex and ever-evolving landscape, with a multitude of investment opportunities available. Among these, options trading stands out as a sophisticated yet potentially lucrative avenue for those seeking to capitalize on market fluctuations. At its core, options are financial instruments that provide the buyer with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specified expiration date. To navigate this dynamic market effectively, it is essential to grasp the concept of option volatility and its influence on pricing. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of option volatility and pricing, empowering you with the knowledge and insights necessary to make informed trading decisions.
Image: productionsdigital.weebly.com
Understanding Option Volatility
Option volatility, often measured using the Volatility Index (VIX), is a key determinant of option pricing. It measures the expected fluctuations in the price of the underlying asset over the life of the option contract. A high volatility indicates a greater likelihood of substantial price movements, while a low volatility suggests a more stable market.
The Impact of Volatility on Option Pricing
The level of volatility has a significant impact on option pricing. Higher volatility generally leads to higher option prices because it increases the probability of the option moving in favor of the buyer. This is because the buyer of an option is essentially betting that the underlying asset will experience price fluctuations within the option’s lifespan.
Types of Option Volatility
Volatility can be categorized into two main types: historical volatility and implied volatility. Historical volatility measures the actual price fluctuations of the underlying asset over a specific past period, while implied volatility reflects the market’s expectations of future volatility based on the prices of options with various expiration dates.
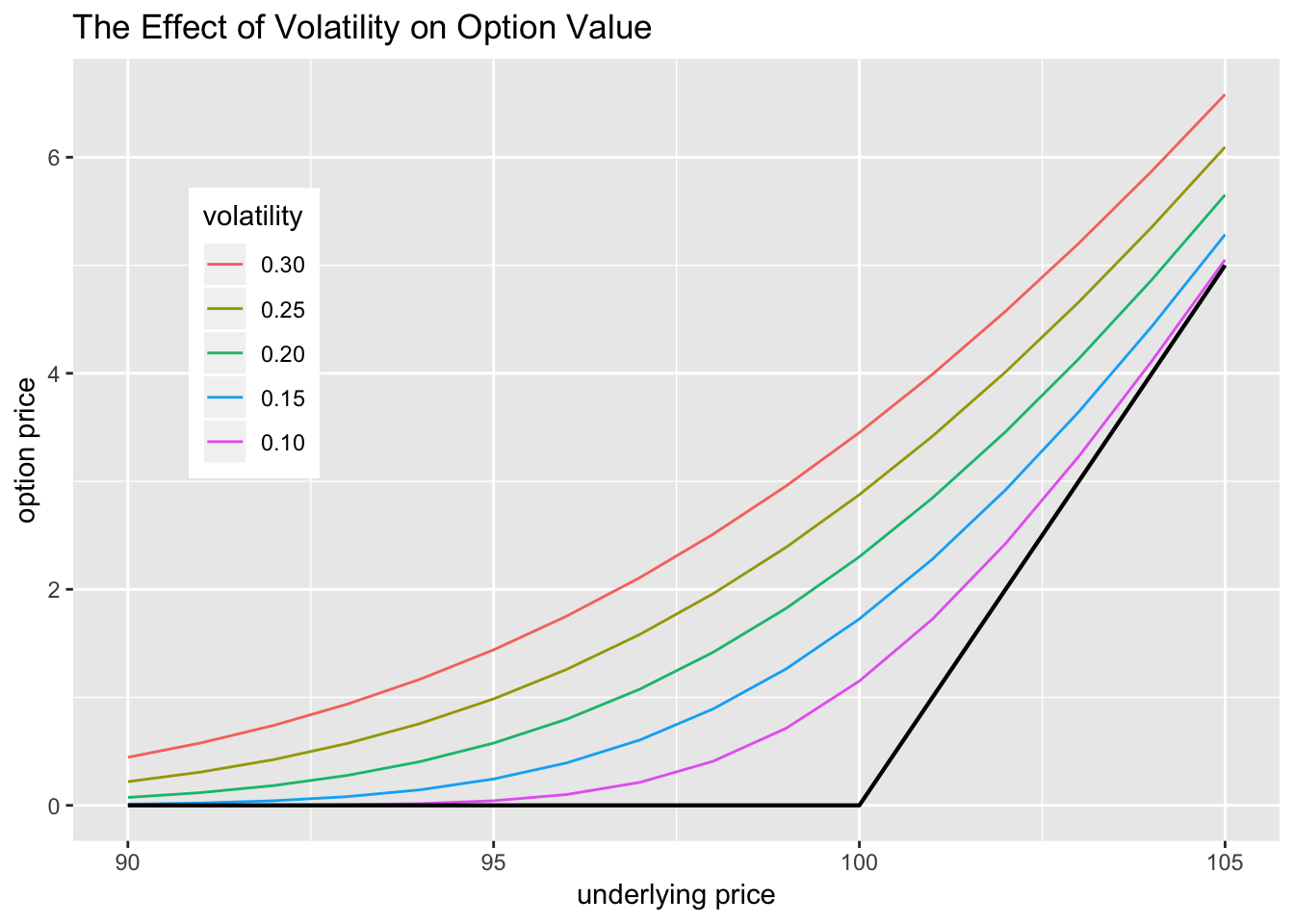
Image: blogs.cornell.edu
The Importance of Implied Volatility
Implied volatility is a crucial factor in option pricing, as it allows traders to gauge the market’s sentiment about the potential price movements of the underlying asset. Traders can analyze implied volatility to identify trading opportunities, such as buying options with undervalued implied volatility or selling options with overvalued implied volatility.
Strategies for Trading Volatility
Traders can employ various strategies to capitalize on option volatility. These strategies include:
- Long Volatility: Buying options and expecting volatility to rise.
- Short Volatility: Selling options and expecting volatility to fall.
- Volatility Arbitrage: Taking advantage of discrepancies in implied volatility between different options contracts.
- Straddle: Buying both a call and a put option on the same underlying asset at the same strike price and expiration date.
Option Volatility And Pricing Pdf
Conclusion
Option volatility is a fundamental aspect of options trading. By understanding the concept of volatility and its impact on pricing, traders can make more informed decisions. The ability to assess volatility accurately can enhance the potential for successful trading in the options market. It is crucial for traders to continuously monitor volatility levels and incorporate them into their trading strategies to navigate the ever-changing financial landscape effectively.







