In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, Site-to-Site VPN (Virtual Private Network) has emerged as a crucial technology for businesses seeking secure and reliable connectivity between their on-premises networks and cloud environments. However, for networks with dynamically assigned IP addresses, configuring Site-to-Site VPN can introduce challenges. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to establishing Site-to-Site VPN with dynamic IP addresses, ensuring seamless and secure network connectivity.
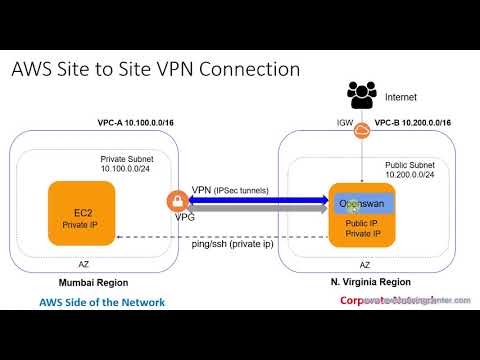
Image: laptrinhx.com
Understanding Site-to-Site VPN
A Site-to-Site VPN is a private network established between two or more physical locations, typically an on-premises network and a cloud environment. It operates over the public internet, encapsulating traffic in secure tunnels encrypted using industry-standard protocols. This secure connection allows users and applications to access remote resources as if they were on the same physical network.
Dynamic IP Address Challenges
Many networks use dynamic IP addresses, which are assigned automatically by a DHCP server and can change over time. This poses a challenge for Site-to-Site VPN configurations because the VPN endpoints need to be able to locate each other to establish the connection. Traditional VPN approaches, which rely on static IP addresses, are not suitable for networks with dynamic IP addresses.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) for Resolution
To overcome the challenge of dynamic IP addresses, Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is commonly employed. DDNS is a service that tracks the changing IP addresses of hosts and maps them to a resolvable domain name. By using a DDNS service, the VPN endpoints can refer to the domain name instead of a specific IP address, thus allowing the VPN connection to remain active even if the IP addresses change.
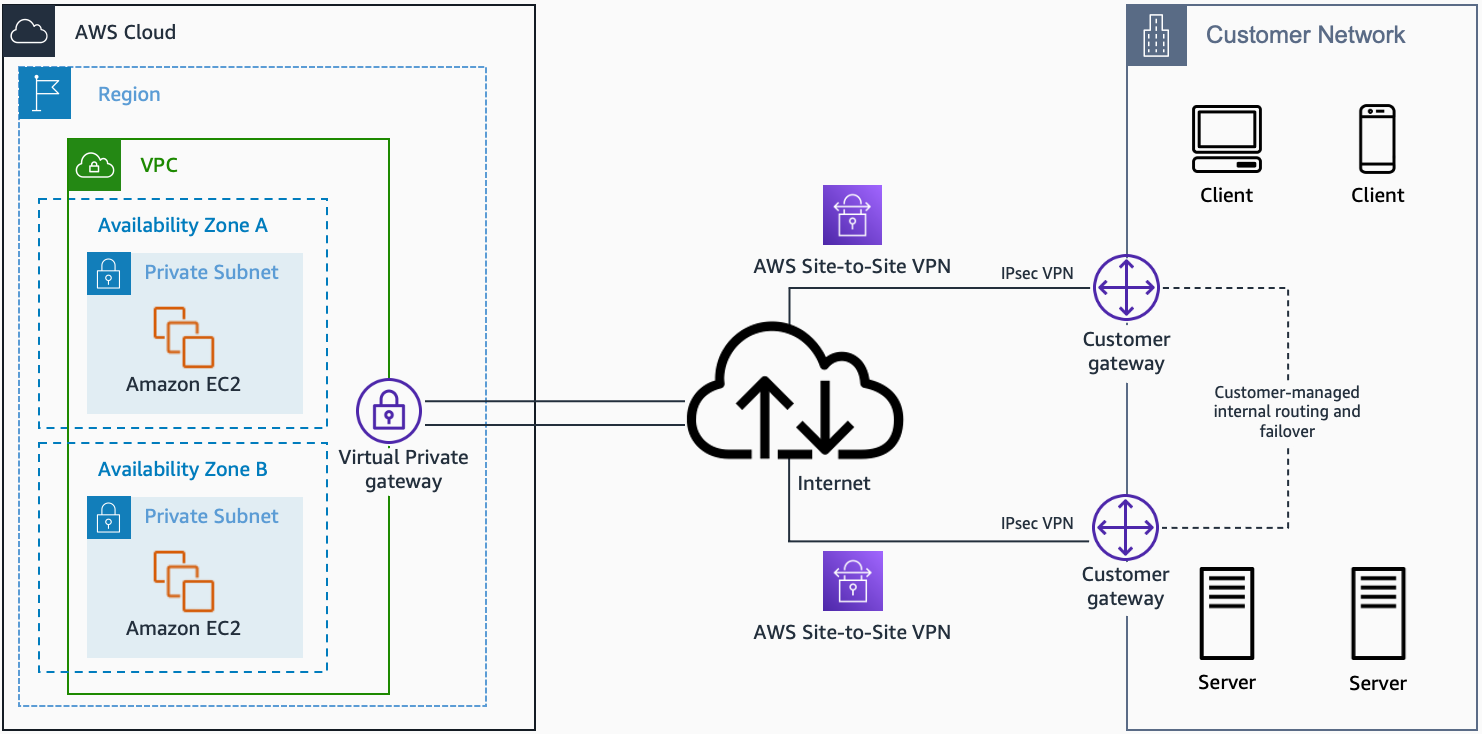
Image: chinomsoikwuagwu.com
Configuring Site-to-Site VPN with Dynamic IP
The general steps involved in configuring Site-to-Site VPN with dynamic IP addresses include:
- Choose a DDNS provider and configure it for your network.
- Create a VPN gateway in your cloud environment and configure it to use the DDNS domain name.
- Configure a VPN connection on your on-premises network, specifying the DDNS domain name of the VPN gateway.
- Establish the VPN connection and verify connectivity.
Benefits of Dynamic IP Site-to-Site VPN
Using Site-to-Site VPN with dynamic IP addresses provides several advantages:
- Flexibility: It allows for seamless connectivity even when IP addresses change dynamically.
- Simplified Management: Eliminates the need to manually update IP addresses in VPN configurations.
- Improved Reliability: Ensures continuous connectivity without requiring constant attention to IP address changes.
- Cost-Effective: DDNS services are typically affordable, offering a cost-efficient solution.
Aws Site To Site Vpn Dynamic Ip
https://youtube.com/watch?v=h8b59GWP0sk
Conclusion
Establishing Site-to-Site VPN with dynamic IP addresses is essential for organizations seeking secure and reliable connectivity to cloud environments. By employing Dynamic DNS services, businesses can overcome the challenges posed by dynamic IP addresses and enjoy the benefits of seamless network connectivity. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the process, empowering readers to configure Site-to-Site VPN effectively and harness its transformative potential.







