The financial world operates on a complex network of indices that mirror the performance of various market segments. Among the most widely used is the market value weighted index, a cornerstone measure that encapsulates the health of a specific market or sector. Understanding the formula behind this index is paramount to unraveling its inner workings and gaining actionable insights into the financial landscape.
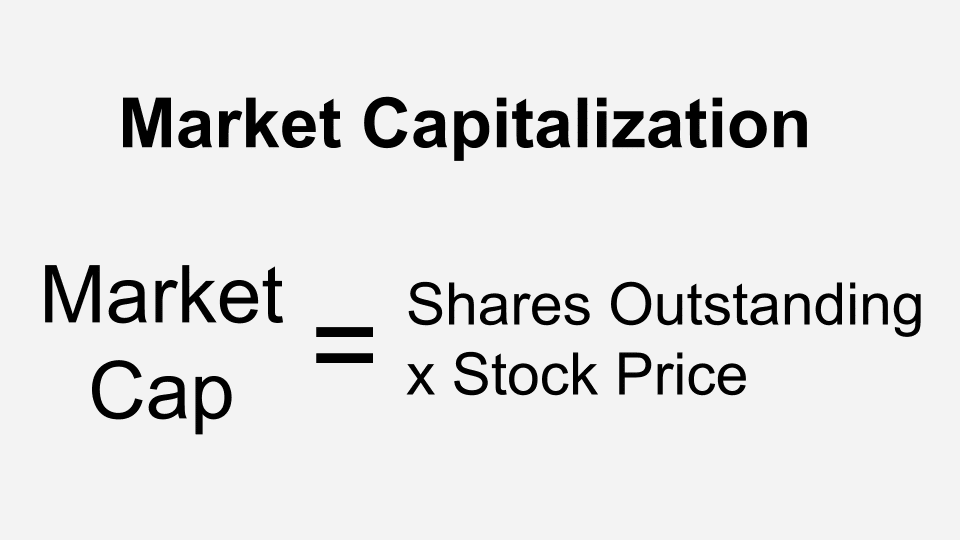
Image: stockanalysis.com
Delving into the Market Value Weighted Index
A market value weighted index represents a basket of assets, typically stocks, whose collective value fluctuates based on the market capitalization of its constituents. Market capitalization is simply the total value of a company’s outstanding shares and is calculated by multiplying the current share price by the number of outstanding shares. In a market value weighted index, the weight assigned to each stock corresponds to its market capitalization.
The direct relationship between market capitalization and index weighting implies that large-cap stocks, those with higher market values, exert a more significant influence on the index’s overall movement. This weighting scheme mirrors the reality of market dynamics, where larger companies tend to have a greater sway in shaping market performance.
The Formula Unveiled
The market value weighted index formula is a simple yet powerful mechanism for capturing market movements. It calculates the index value (I) as follows:
I = (M1 * W1 + M2 * W2 + ... + Mn * Wn) / DWhere:
- M1, M2, …, Mn are the market values of each constituent stock
- W1, W2, …, Wn are the corresponding weights assigned to each stock based on their market capitalization
- D is a divisor that normalizes the index value (often a constant or the sum of all weights)
By combining the market values and weights of individual stocks, this formula distills the collective performance of the index into a single, comprehensive metric. It provides investors with a snapshot of how the market as a whole is faring, dominated by the performance of its largest constituents.
The Significance of Index Weighting
The weighting scheme employed in market value weighted indices has significant implications for their performance. By overweighting stocks with larger market capitalizations, these indices favor established, mature companies that are often less volatile. This bias toward stability may be attractive to risk-averse investors seeking long-term growth.
However, it also means that market value weighted indices may be less responsive to the performance of smaller companies with potentially higher growth potential. This is because, despite their impressive returns, smaller companies carry a smaller weight in the index, resulting in a muted impact on the overall index movement.
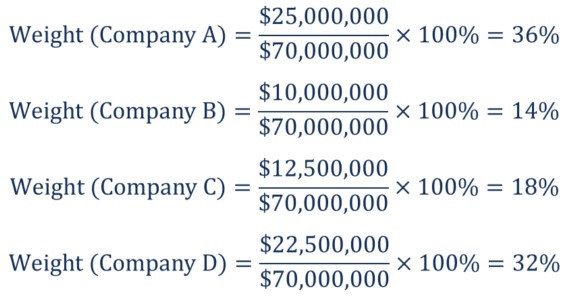
Image: www.investorgreg.net
Applications in the Financial Landscape
Market value weighted indices are ubiquitous in the financial arena, serving as benchmarks for asset performance and guiding investment decisions. They are frequently used to:
- Track market performance over time
- Create passively managed index funds
- Measure portfolio performance against market benchmarks
- Gauge economic conditions and industry trends
Examples of well-known market value weighted indices include the S&P 500 (large-cap stocks in the US), the FTSE 100 (large-cap stocks in the UK), and the Nikkei 225 (large-cap stocks in Japan).
Continuous Evolution and Refinements
The realm of market value weighted indices is constantly evolving, with refinements and innovations shaping their usage and effectiveness. Some notable variations include:
- Price Weighted Indices: Assign weights based on the stock price instead of market capitalization.
- Equal Weighted Indices: Assign equal weights to all constituents, regardless of size.
- Modified Market Cap Weighted Indices: Adjust weights based on factors such as sales, earnings, or dividends.
Market Value Weighted Index Formula
Conclusion
The market value weighted index formula is an essential tool for understanding financial markets. By weighting stocks according to their market capitalization, it provides a comprehensive gauge of market performance, heavily influenced by the performance of industry leaders. Whether tracking market trends, managing investments, or gauging economic conditions, market value weighted indices offer a powerful lens for navigating the ever-changing financial landscape. As the market continues to innovate, we can expect further refinements and advancements to these indices, ensuring their continued relevance in analyzing and leveraging financial markets.







