Margin is a critical concept in the foreign exchange (Forex) market, enabling traders to control significantly more capital than they possess. It represents a loan from the broker, allowing traders to multiply the potential returns on their trades. Understanding margin is essential for effective Forex trading and risk management.
Image: blog.fxcc.com
Traditionally, Forex trades required substantial capital to make meaningful profits. Margin trading eliminates this barrier, allowing traders to access larger positions with a fraction of the required funds. However, it’s crucial to note that margin trading amplifies both potential profits and losses, emphasizing prudent risk management.
The Mechanics of Margin
Margin is essentially a ratio expressed as a percentage, such as 100:1. If a trader has $1,000 and a margin of 100:1, they can open a position worth $100,000. The $1,000 represents the margin requirement, which is held by the broker as collateral. The difference between the position value and the margin requirement is known as the leverage. In this case, it’s 100:1.
Leverage: A Double-Edged Sword
Leverage is the power of margin trading, enabling traders to amplify their gains. However, it also amplifies potential losses. Using the example above, a 1% appreciation in the underlying asset will yield a 1% return on the trader’s initial investment of $1,000. However, a 1% depreciation will result in a 1% loss on the $1,000, potentially wiping out the entire investment.
Margin Calls and Stop-Out
To protect brokers, margin calls and stop-out levels are implemented. A margin call occurs when the equity in a trader’s account falls below the required margin level. The trader is then required to deposit additional funds or close some of their positions to meet the margin requirements. If the trader fails to meet a margin call, the broker may forcibly close their positions, known as a stop-out.
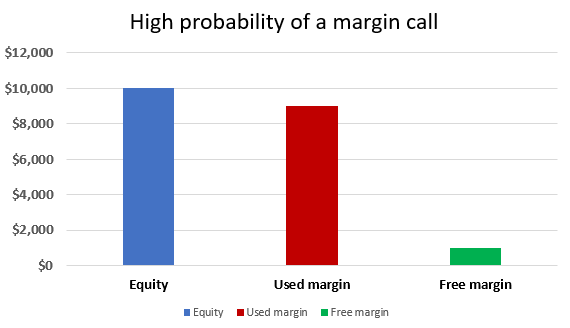
Image: blog.cabanacapitals.com
Managing Margin Risk
Effective margin risk management revolves around responsible trading practices. Here are a few tips:
- Choose Appropriate Leverage: The ideal margin ratio depends on the trader’s risk tolerance and trading strategy. Beginners should start with lower leverage.
- Maintain Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders limit potential losses by automatically closing a position when it reaches a predefined price level.
- Monitor Positions Regularly: Keep a close eye on open positions to assess their performance and adjust the leverage as needed.
- Diversify Trades: Spreading risk across multiple currency pairs can mitigate losses from adverse market movements in any one currency.
In Forex What Is Margin
Conclusion
Margin trading in Forex empowers traders with the ability to access larger positions with limited capital. While it can magnify potential profits, it also amplifies risks. By understanding the mechanics of margin and implementing sound risk management strategies, traders can harness the power of leverage while minimizing potential losses. Remember, responsible margin trading is key to successful Forex endeavors.







