Inflation is a critical economic indicator that measures the rate at which prices for goods and services increase over time. The inflation rate serves as a barometer of the overall health of an economy and can impact consumers, businesses, and the government’s economic policies.
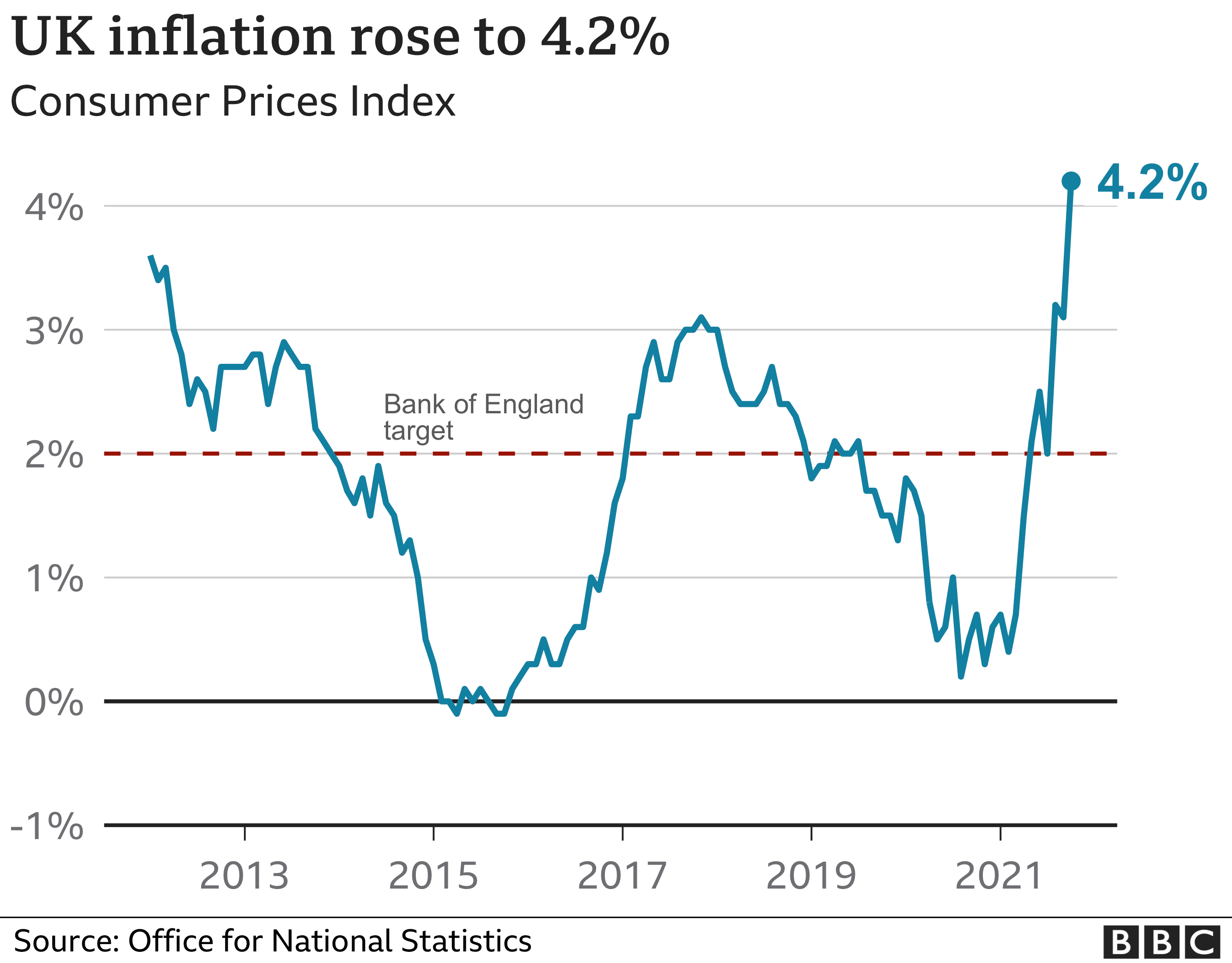
Image: www.bbc.com
In the UK, the inflation rate is calculated by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) using the Consumer Prices Index (CPI) and the Retail Prices Index (RPI). The CPI measures the change in prices for a basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households, while the RPI includes additional costs such as mortgage interest payments.
Historical Perspective of Inflation in the UK
Understanding the historical perspective of inflation in the UK provides valuable insights into the country’s economic performance over time. Inflation rates have fluctuated significantly over the decades, ranging from periods of high inflation (e.g., the 1970s) to periods of low inflation (e.g., the 1990s).
During the 1970s, the UK experienced a severe economic crisis known as the “oil crisis,” which led to a sharp increase in inflation. The inflation rate peaked at 24.2% in August 1975, primarily driven by rising oil prices and currency depreciation.
Understanding Inflation: Its Causes and Consequences
Inflation can be caused by various factors, including rising demand, supply shocks, and monetary policy measures. When demand for goods and services exceeds supply, prices tend to increase. Supply shocks, such as natural disasters or disruptions in global supply chains, can also lead to higher inflation.
Excessive inflation can have adverse consequences for an economy. It erodes the value of savings, reduces consumer purchasing power, and hampers economic growth. In extreme cases, hyperinflation can occur, where prices rise exponentially and lead to monetary instability.
Monitoring and Managing Inflation in the UK
The Bank of England (BOE) is responsible for setting monetary policy in the UK, including managing the inflation rate. The BOE’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability and aims to keep the inflation rate within a target range of 2%. This is achieved by using monetary policy tools, such as setting interest rates and controlling the money supply.
The UK’s inflation rate has remained relatively low in recent years, averaging around 2% since 2009. However, the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine have contributed to a recent surge in inflation.
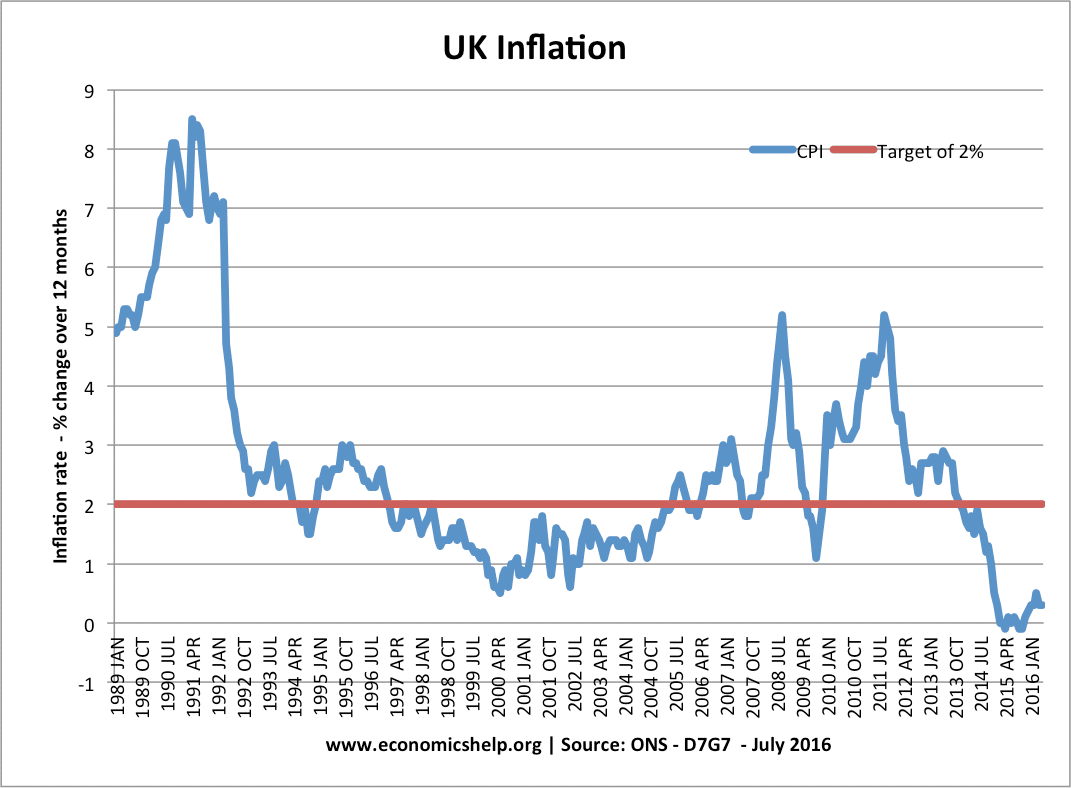
Image: www.economicshelp.org
Tips and Expert Advice for Dealing with Inflation
Knowing how to deal with inflation and its impact can help individuals and businesses navigate economic uncertainty. Here are some expert recommendations:
- Invest in inflation-linked assets: Assets such as index-linked bonds or real estate can help protect investments from rising prices.
- Negotiate higher wages or salaries: If inflation is eroding your purchasing power, consider negotiating a pay increase to maintain your standard of living.
- Cut unnecessary expenses: Review your budget and identify areas where you can reduce spending to offset increased costs.
- Shop around for lower prices: Compare prices across different retailers and online marketplaces to find the best deals on goods and services.
- Consider additional income streams: Explore opportunities for extra income, such as part-time work, freelance projects, or selling unwanted possessions.
FAQ on Inflation in the UK
What is the current inflation rate in the UK?
As of October 2022, the UK’s inflation rate is 11.1%, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
What is the difference betweenCPI and RPI?
The CPI measures the change in prices for a basket of goods and servicescommonly purchased by households, while the RPI also includes additional costs such as mortgage interest payments.
What can cause high inflation?
Various factors can lead to high inflation, including increasing demand, supply shocks, and expansionary monetary policy.
What are the consequences of inflation?
Inflation can erode savings, reduce consumer purchasing power, and hamper economic growth.
What is the best way to manage inflation?
Managing inflation requires a comprehensive approach involving monetary policy, fiscal policy, and measures to increase productivity.
Inflation Rate Uk Chart
Conclusion
Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that can have a significant impact on consumers, businesses, and the economy as a whole. The UK’s inflation rate, measured by the CPI and the RPI, has fluctuated over time and is currently at an elevated level of 11.1%. Understanding the causes, consequences, and strategies for dealing with inflation can provide valuable insights for individuals and policymakers alike. By monitoring economic data, utilizing expert advice, and adopting prudent financial practices, we can navigate the complexities of inflation and mitigate its potential negative consequences.
Do you find the topic of inflation rate UK chart engaging? Share your thoughts in the comments below.







