Introduction:
In the dynamic realm of finance, understanding the intricacies of various trading instruments is essential for navigating the complex markets successfully. One such instrument that has gained significant traction in recent years is the Contract for Difference (CFD). Its versatility and potential for high returns have made CFDs popular among individual traders and institutional investors alike.
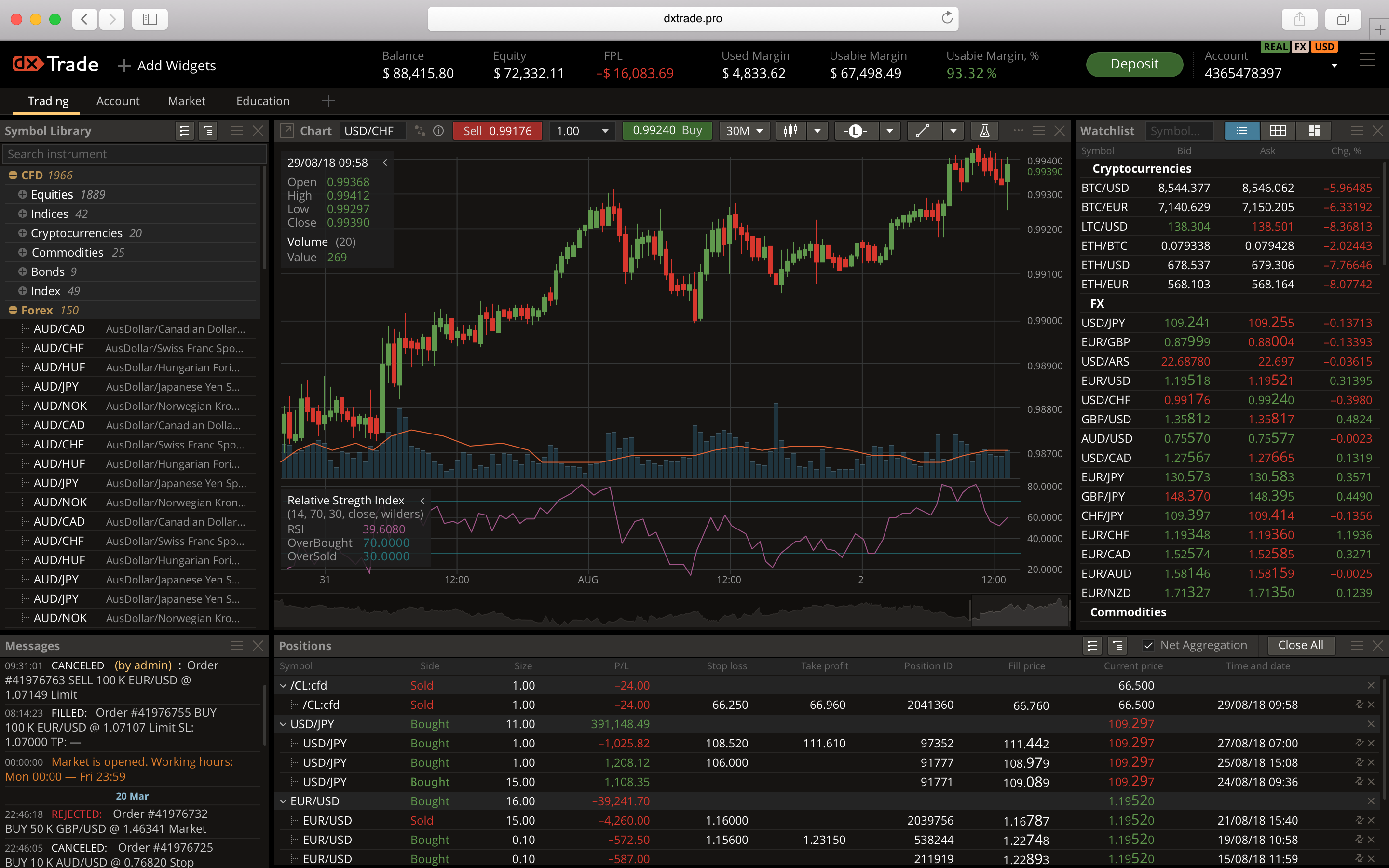
Image: devexperts.com
Understanding CFDs:
A CFD is a financial contract between two parties, the trader and the broker, that allows the trader to speculate on the price movements of an underlying asset without actually owning the asset itself. The underlying asset can be stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, or even cryptocurrencies. When entering into a CFD contract, the trader essentially agrees to exchange the difference in value of the underlying asset from the point of entry to the point of exit.
Unlike traditional stock trading, where ownership of the underlying asset is acquired, CFDs provide exposure to the price changes of the asset, enabling traders to capitalize on both rising and falling markets. This inherent leverage in CFDs makes them attractive to traders seeking to maximize their returns on capital invested.
Key Features of CFDs:
a. Leverage: One of the most notable characteristics of CFDs is the use of leverage, allowing traders to control a larger position with a relatively small initial investment. Leverage can significantly magnify profits, but it also amplifies potential losses, making risk management crucial.
b. Short Selling: Another key feature of CFDs is the ability to engage in short selling. Unlike traditional stock trading, CFDs allow traders to speculate on price declines by opening a short position, enabling them to profit from downward price movements.
c. Diversification: CFDs offer a wide range of underlying assets, providing traders with numerous opportunities to diversify their portfolios and manage risk across different markets and asset classes.
Types of CFDs:
a. Index CFDs: Track the performance of a specific stock market index, such as the S&P 500 or FTSE 100.
b. Stock CFDs: Provide exposure to the price fluctuations of individual company stocks.
c. Currency CFDs (Forex Pairs): Centered around currency pairs, allowing traders to speculate on exchange rate movements.
d. Commodity CFDs: Track the prices of physical commodities like oil, gold, and wheat.
e. Cryptocurrency CFDs: Offer access to trading cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum without owning the underlying digital assets.
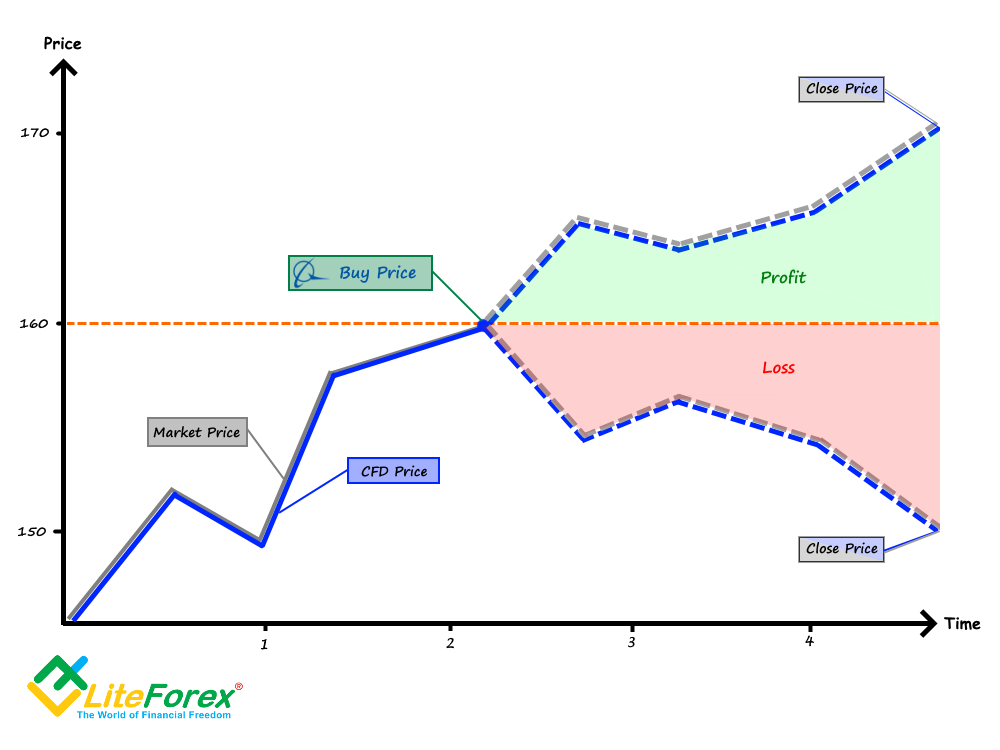
Image: www.liteforex.com
The Benefits of Trading CFDs:
a. Flexibility: CFDs provide traders with a flexible instrument that can be employed for various trading strategies, including long-term investments, short-term trading, and hedging.
b. Cost-Effective: CFDs typically involve lower trading costs compared to traditional instruments like stocks, as they eliminate the need for physical delivery or settlement.
c. Unlimited Profit Potential: CFDs allow traders to profit from both rising and falling markets, creating the potential for significant returns.
Expert Advice for CFD Trading:
a. Risk Management: Implement robust risk management strategies to limit potential losses, including using stop-loss orders and managing leverage prudently.
b. Strategy Development: Develop a well-defined trading strategy based on technical or fundamental analysis, considering factors like market conditions and risk tolerance.
c. Education and Practice: Educate yourself thoroughly about CFDs, their risks, and trading techniques before entering live markets. Demo accounts provide a safe environment for practicing and refining your skills.
FAQ on CFDs:
a. Q. What are the risks involved in CFD trading?
- A. CFDs carry inherent risks, including leverage, volatility, and potential for losses to exceed initial investment.
b. Q. How do I get started with CFD trading?
- A. Choose a regulated broker, open a trading account, and fund it to commence trading.
c. Q. What are the tax implications of CFD trading?
- A. Tax implications vary depending on jurisdiction and individual circumstances; consult with a tax advisor for specific guidance.
What Is Cfd In Trading
Conclusion:
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) have emerged as a dynamic and popular financial instrument, offering traders the potential for substantial returns and the flexibility to speculate on various underlying assets. Understanding the key features, types, and benefits of CFDs is essential for aspiring traders. Arming oneself with education, prudent risk management, and a well-defined strategy can enhance the likelihood of successful CFD trading. Are you ready to explore the exciting world of CFDs?







